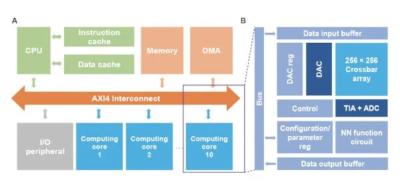
Researchers design a versatile compact RRAM model that can model different types of RRAM devices
Researchers from The University of California, Berkeley, designed a new versatile compact RRAM model that can model different types of RRAM devices such as oxide-RRAM (OxRAM) and conducting-bridge-RRAM (CBRAM).
The researchers say that their new model unifies the switching mechanisms of these RRAMs into a single framework. The researchers showcase the model’s accuracy in reproducing published experimental device DC and transient characteristics of various RRAM structures. They also demonstrated the model’s efficacy in capturing RRAM variability and conducting 1T1R circuit simulations.